Cloud computing allows organizations to focus on their core business and leave unwanted work like IT infrastructure capacity planning, procurement, and maintenance to cloud providers. As cloud computing has grown exponentially in recent years, different models and strategies have surfaced to help meet the specific needs of organizations as per their user base. Each type of cloud computing model provides you with additional flexibility and management. There are many ways to classify cloud services, and understanding the differences between them helps you decide what set of services is suitable for your application workload. In this section, we will cover a common classification. Cloud services can be categorized as follows:
As the names indicate, each model provides a service at a different stack level.Each of these solutions has its advantages and disadvantages. It is essential to fully understand these tradeoffs to select the best option for your organization:
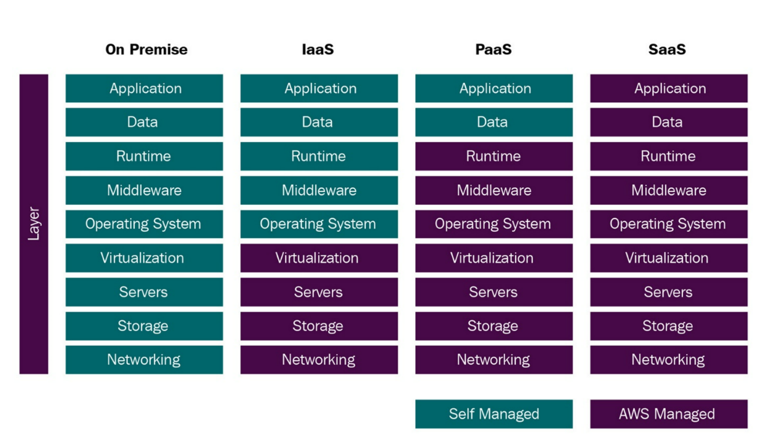
As you can see in the preceding image, the amount of services managed by yourself or AWS determines how the stack will be classified. On one extreme, we have an on-premises environment, where all the infrastructure is located in your own data center. On the other extreme, we have a SaaS architecture, where all the infrastructure is located on the cloud. The following sections will explore the advantages and disadvantages of using each and examples of services under each classification.
Cloud infrastructure services, also known as IaaS, comprise highly flexible, fault-tolerant compute and storage resources. IaaS provides access and full management and monitoring of compute, storage, networking, and other miscellaneous services. IaaS enables enterprises to use resources on an as-needed basis, so they don’t need to purchase the equipment.IaaS leverages virtualization technology. AWS allows you to quickly provision hardware through the AWS console, using the Command-Line Interface (CLI) or using an API, among other methods. By using an IaaS platform, a business can provide a whole host of resources and functionality with their current infrastructure without the headache of physically maintaining it. From a user perspective, they might not even be aware that the backend services are being provided by an IaaS platform instead of being a company-owned data center.As you saw in Figure 2.1, when using the IaaS solution, you are responsible for managing more aspects of the stack such as applications, runtime, operating systems, middleware, and data. However, AWS will manage servers, hard drives, networking, virtualization, databases, and file storage in these cases.You will now learn the advantages and disadvantages of IaaS services and look at some IaaS use cases; finally, you will see some examples of IaaS offerings.